定时器简介
内核时间管理简介
Linux内核使用定时器中断来计时。中断周期性产生的频率就是系统频率,也叫做节拍率(tick rate)(有的资料也叫系统频率)。系统节拍率是可以设置的,单位是 Hz,在编译 Linux 内核的时候可以通过图形化界面设置系统节拍率,按照如下路径打开配置界面。
-> Kernel Features
-> Timer frequency (<choice> [=y])
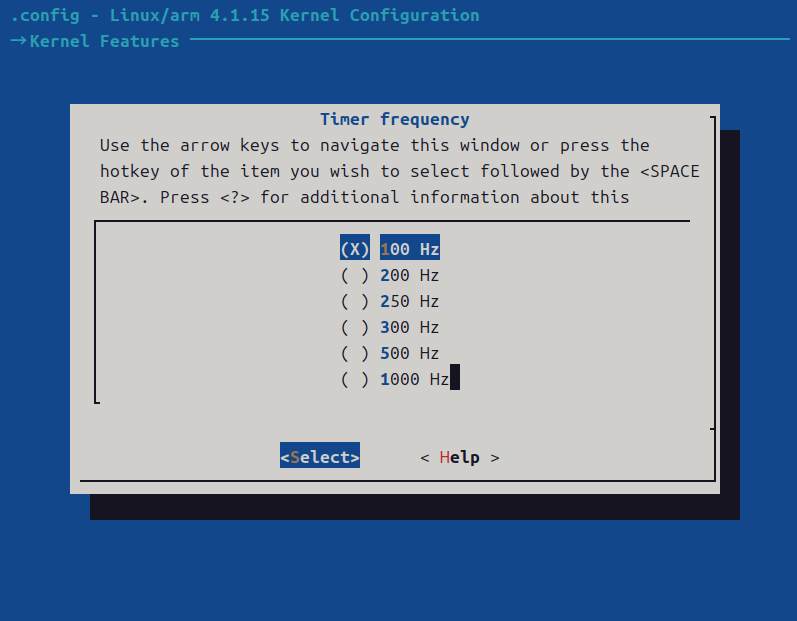
高节拍率会提高系统时间精度,但是高节拍率会导致中断的产生更加频繁,频繁的中断会加剧系统的负担。一般来说,使用100M的系统节拍率就基本满足日常需求了。
Linux内核使用全局变量jiffies来记录系统启动以来的系统节拍数,系统启动的时候会将 jiffies 初始化为 0。在64位的系统中使用的是jiffies_64。表示的范围更广了。jiffies是jiffies_64的低32bit。不管是 32 位的系统还是 64 位系统,都可以使用 jiffies。
32位的jiffies有绕回风险,为此linux内核提高了如下函数来处理绕回。
下面两个相比于上面上个增加了等于的条件。如果 unkown 超过 known 的话, time_after 函数返回真,否则返回假
为了方便开发, Linux 内核还提供了几个 jiffies 和 ms、 us、 ns 之间的转换函数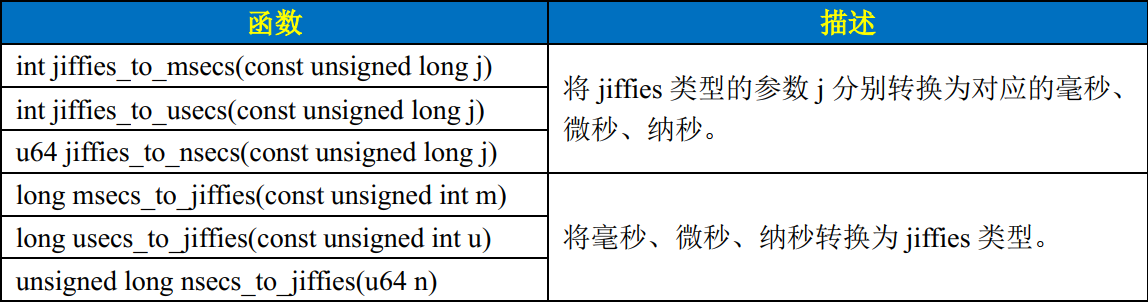
内核定时器简介
Linux 内核定时器采用系统时钟来实现,并不是硬件定时器。使用很简单,只需要提供超时时间(相当于定时值)和定时处理函数即可。当超时时间到了以后设置的定时处理函数就会执行。
内核定时器并不是周期性运行的,超时以后就会自动关闭,因此如果想要实现周期性定时,那么就需要在定时处理函数中重新开启定时器。
Linux 内核使用 timer_list 结构体表示内核定时器, timer_list 定义在文件include/linux/timer.h 中,定义如下
struct timer_list {
struct list_head entry;
unsigned long expires; /* 定时器超时时间,单位是节拍数 */
struct tvec_base *base;
void (*function)(unsigned long); /* 定时处理函数 */
unsigned long data; /* 要传递给 function 函数的参数 */
int slack;
};要使用内核定时器首先要先定义一个 timer_list 变量,表示定时器。
定义好定时器以后还需要通过一系列的 API 函数来初始化此定时器
init_timer 函数
init_timer 函数负责初始化 timer_list 类型变量,当我们定义了一个 timer_list 变量以后一定要先用 init_timer 初始化一下。函数原型如下:
//timer:要初始化定时器
void init_timer(struct timer_list *timer) add_timer 函数
add_timer 函数用于向 Linux 内核注册定时器,使用 add_timer 函数向内核注册定时器以后,定时器就会开始运行。函数原型如下:
//timer:要注册的定时器
void add_timer(struct timer_list *timer) del_timer 函数
del_timer 函数用于删除一个定时器,不管定时器有没有被激活,都可以使用此函数删除。在多处理器系统上,定时器可能会在其他的处理器上运行,因此在调用 del_timer 函数删除定时器之前要先等待其他处理器的定时处理器函数退出。也就是说,管你有没有用直接干掉。函数原型如下:
//timer:要删除的定时器
//返回值: 0,定时器还没被激活; 1,定时器已经激活。
int del_timer(struct timer_list * timer) del_timer_sync 函数
del_timer_sync 函数是 del_timer 函数的同步版,等到定时器没有使用状态下,才删除。函数原型如下:
//timer:要删除的定时器。
//返回值: 0,定时器还没被激活; 1,定时器已经激活。
int del_timer_sync(struct timer_list *timer) mod_timer 函数
mod_timer 函数用于修改定时值,如果定时器还没有激活的话, mod_timer 函数会激活定时器,函数原型如下:
//timer:要修改超时时间(定时值)的定时器。
//expires:修改后的超时时间。
//返回值: 0,调用 mod_timer 函数前定时器未被激活; 1,调用 mod_timer 函数前定时器已被激活
int mod_timer(struct timer_list *timer, unsigned long expires)Linux内核短延时函数
Linux 内核提供了毫秒、微秒和纳秒延时函数。API如下所示
程序编写
设备树修改
驱动程序编写
#include "linux/types.h"
#include "linux/kernel.h"
#include "linux/delay.h"
#include "linux/ide.h"
#include "linux/init.h"
#include "linux/module.h"
#include "linux/errno.h"
#include "linux/gpio.h"
#include "linux/cdev.h"
#include "linux/device.h"
#include "linux/of.h"
#include "linux/of_address.h"
#include "linux/of_gpio.h"
#include "linux/semaphore.h"
#include "linux/timer.h"
#include "asm/mach/map.h"
#include "asm/uaccess.h"
#include "asm/io.h"
#define TIMER_CNT 1
#define TIMER_NAME "timer"
#define CLOSE_CMD (_IO(0xEF, 0x01))
#define OPEN_CMD (_IO(0xEF, 0x02))
#define SETPERIOD_CMD (_IO(0xEF, 0x03))
#define LEDON 1
#define LEDOFF 0
struct timer_dev{
dev_t devid;
struct cdev cdev;
struct class *class;
struct device *device;
int major;
int minor;
struct device_node *nd;
int led_gpio;
int timeperiod;
struct timer_list timer;
spinlock_t lock;
};
struct timer_dev timerdev;
static int led_init(void)
{
int retvalue = 0;
timerdev.nd = of_find_node_by_path("/led");
if(timerdev.nd == NULL){
return -EINVAL;
}
timerdev.led_gpio = of_get_named_gpio(timerdev.nd, "led-gpio", 0);
if(timerdev.led_gpio < 0){
printk("can't get led\r\n");
return -EINVAL;
}
gpio_request(timerdev.led_gpio, "led");
retvalue = gpio_direction_output(timerdev.led_gpio, 1);
if(retvalue < 0){
printk("can't set gpio\r\n");
return -EINVAL;
}
return 0;
}
static void led_deinit(void)
{
gpio_free(timerdev.led_gpio);
}
static int timer_open(struct inode *node, struct file *filp)
{
int retvalue = 0;
retvalue = led_init();
if(retvalue < 0){
printk("led init failed\r\n");
return retvalue;
}
filp->private_data = &timerdev;
timerdev.timeperiod = 1000;
return 0;
}
static long timer_unlocked_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
struct timer_dev *dev = (struct timer_dev *)filp->private_data;
int timerperiod;
unsigned long flags;
switch(cmd){
case CLOSE_CMD :{
del_timer_sync(&dev->timer);
break;
}
case OPEN_CMD :{
spin_lock_irqsave(&dev->lock, flags);
timerperiod = dev->timeperiod;
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&dev->lock, flags);
mod_timer(&dev->timer, jiffies + msecs_to_jiffies(timerperiod));
break;
}
case SETPERIOD_CMD :{
spin_lock_irqsave(&dev->lock, flags);
dev->timeperiod = arg;
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&dev->lock, flags);
mod_timer(&dev->timer, jiffies + msecs_to_jiffies(arg));
break;
}
default :{
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
static struct file_operations timer_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = timer_open,
.unlocked_ioctl = timer_unlocked_ioctl,
};
void timer_function(unsigned long arg)
{
struct timer_dev *dev = (struct timer_dev *)arg;
static int sta = 1;
int timerperod;
unsigned long flags;
sta = !sta;
gpio_set_value(dev->led_gpio, sta);
spin_lock_irqsave(&dev->lock, flags);
timerperod = dev->timeperiod;
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&dev->lock, flags);
mod_timer(&dev->timer, jiffies + msecs_to_jiffies(timerperod));
}
static int __init timer_init(void)
{
spin_lock_init(&timerdev.lock);
if(timerdev.major){
timerdev.devid = MKDEV(timerdev.major, 0);
register_chrdev_region(timerdev.devid, TIMER_CNT, TIMER_NAME);
}else{
alloc_chrdev_region(&timerdev.devid, 0, TIMER_CNT, TIMER_NAME);
timerdev.major = MAJOR(timerdev.devid);
timerdev.minor = MINOR(timerdev.devid);
}
timerdev.cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
cdev_init(&timerdev.cdev, &timer_fops);
cdev_add(&timerdev.cdev, timerdev.devid, TIMER_CNT);
timerdev.class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, TIMER_NAME);
if(IS_ERR(timerdev.class)){
return PTR_ERR(timerdev.class);
}
timerdev.device = device_create(timerdev.class, NULL, timerdev.devid, NULL, TIMER_NAME);
if(IS_ERR(timerdev.device)){
return PTR_ERR(timerdev.device);
}
init_timer(&timerdev.timer);
timerdev.timer.function = timer_function;
timerdev.timer.data = (unsigned long)&timerdev;
return 0;
}
static void __exit timer_exit(void)
{
gpio_set_value(timerdev.led_gpio, 1);
del_timer_sync(&timerdev.timer);
// led_deinit();
cdev_del(&timerdev.cdev);
unregister_chrdev_region(timerdev.devid, TIMER_CNT);
device_destroy(timerdev.class, timerdev.devid);
class_destroy(timerdev.class);
}
module_init(timer_init);
module_exit(timer_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("warren");应用程序编写
#include "stdio.h"
#include "unistd.h"
#include "sys/types.h"
#include "sys/stat.h"
#include "fcntl.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "string.h"
#include "linux/ioctl.h"
#define CLOSE_CMD (_IO(0xEF, 0x01))
#define OPEN_CMD (_IO(0xEF, 0x02))
#define SETPERIOD_CMD (_IO(0xEF, 0x03))
int main(int argc, int *argv[])
{
int fd, retvalue;
char *filename;
unsigned int cmd;
unsigned int arg;
unsigned char str[100];
if(argc != 2){
printf("error usage\r\n");
return -1;
}
filename = argv[1];
fd = open(filename, O_RDWR);
if(fd < 0){
printf("can't open %s\r\n", filename);
return -1;
}
while(1){
printf("input cmd:");
retvalue = scanf("%d", &cmd);
if(retvalue != 1){
gets(str);
}
if(cmd == 1)
cmd = CLOSE_CMD;
else if (cmd == 2){
cmd = OPEN_CMD;
}else if(cmd == 3){
cmd = SETPERIOD_CMD;
printf("input timer period:");
retvalue = scanf("%d", &arg);
if(retvalue != 1){
gets(str);
}
}else{
continue;
}
ioctl(fd, cmd, arg);
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}


评论 (0)